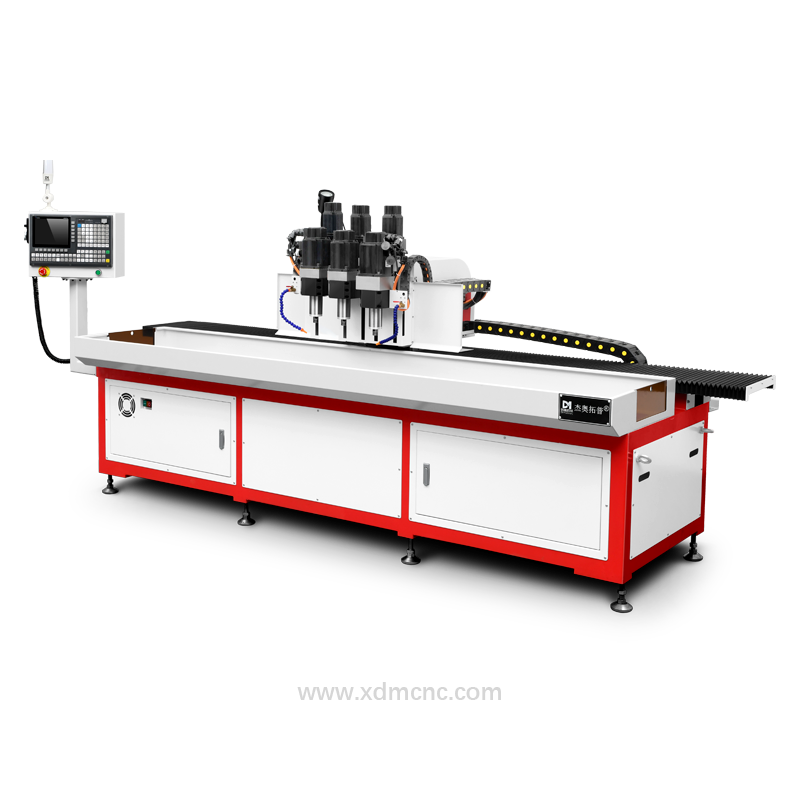
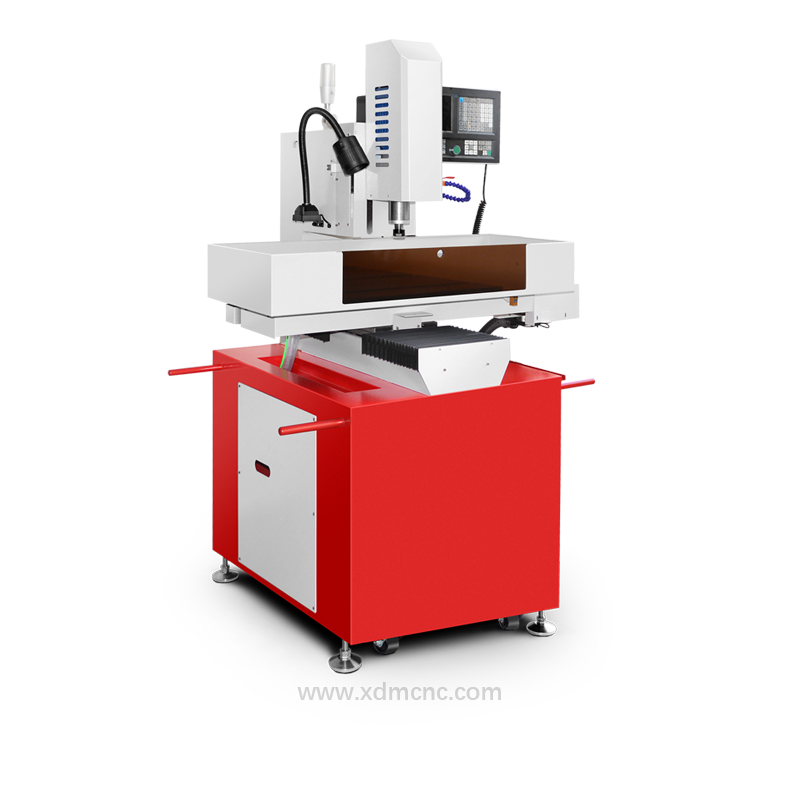
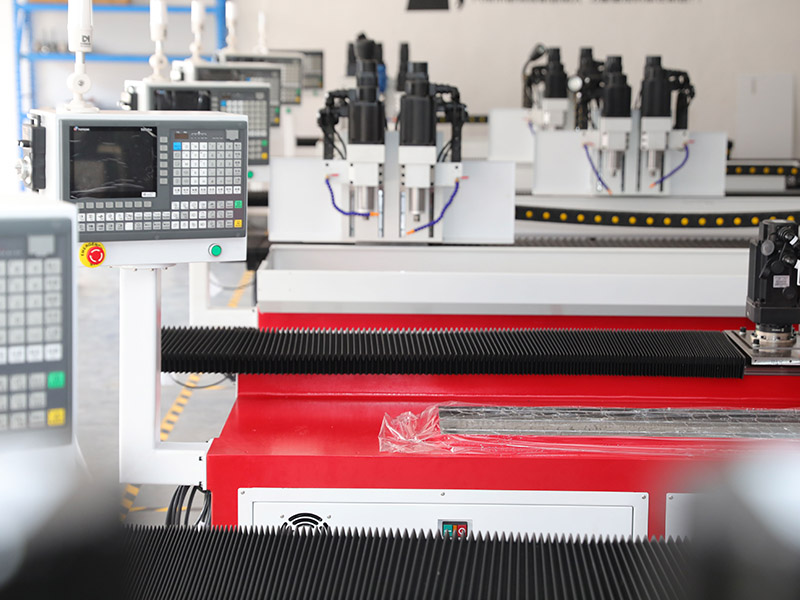
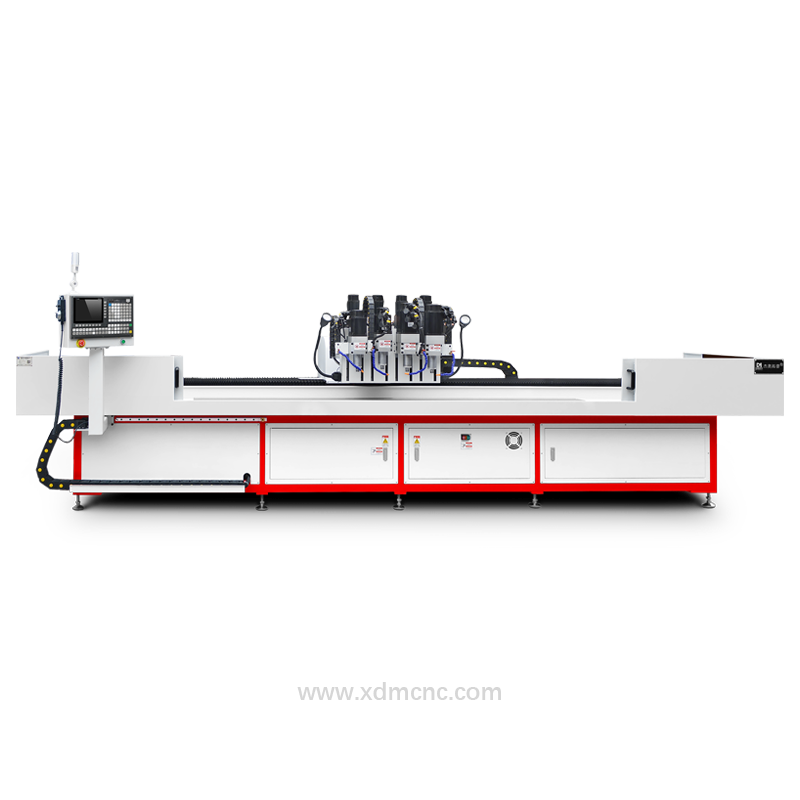
A drill and tap machine is a specialized machining tool designed to perform both drilling and tapping operations in a single setup. These machines enhance efficiency, precision, and consistency in manufacturing processes, making them indispensable in industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and metal fabrication. By automating hole creation and threading, drill and tap machines significantly improve productivity while reducing material waste and operational costs.
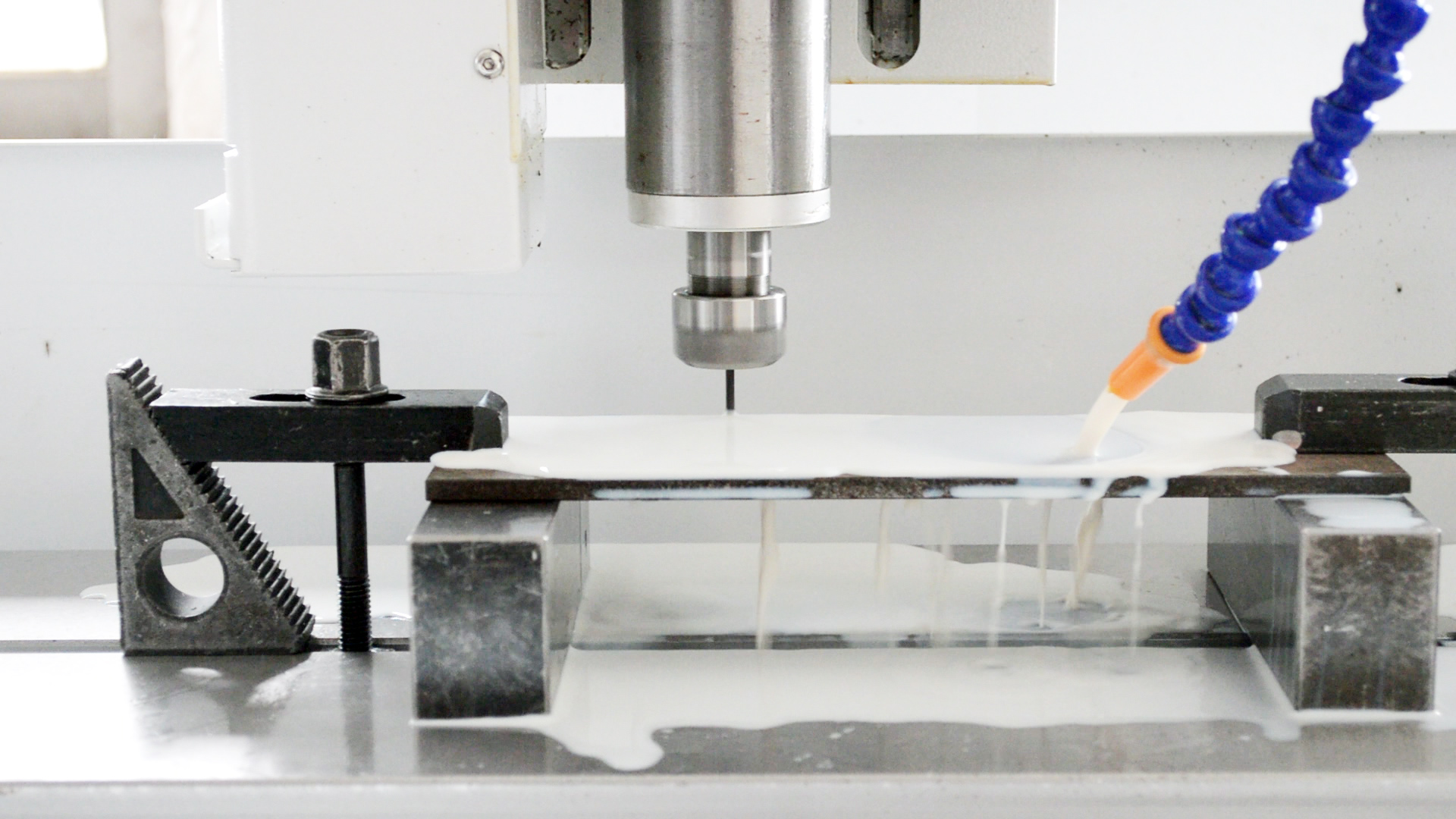

Working Principle
Drill and tap machines operate in two main stages:
Drilling: A high-speed rotating drill bit penetrates the workpiece to create a hole of the desired diameter.
Tapping: A tap tool then follows, cutting internal threads within the pre-drilled hole to accommodate screws or bolts.
These machines can be manually operated, semi-automatic, or fully automated with CNC (Computer Numerical Control) capabilities, ensuring precise and repeatable results for high-volume production.
Types of Drill and Tap Machines
Manual Drill and Tap Machines
Suitable for low-volume or custom machining jobs.
Requires operator control for positioning and feed rate.
Semi-Automatic Drill and Tap Machines
Offers improved consistency with motorized drives and preset feed rates.
Reduces manual labor while maintaining flexibility.
CNC Drill and Tap Machines
Fully automated with computer programming for complex and high-precision tasks.
Ideal for mass production with minimal human intervention.
Advantages of Drill and Tap Machines
Enhanced Efficiency
Combines two machining processes into one, reducing setup time.
Improves workflow by minimizing part handling and repositioning.
High Precision and Consistency
CNC-controlled machines ensure uniform hole depth and thread quality.
Reduces errors compared to manual drilling and tapping.
Versatility
Capable of processing a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites.
Supports different thread sizes and depths based on application requirements.
Cost Savings
Reduces tooling wear and material waste.
Lowers labor costs through automation and increased throughput.
Industrial Applications
Automotive Manufacturing: Used for engine components, chassis, and assembly fixtures requiring threaded holes.
Aerospace Industry: Ensures high-precision drilling and tapping for aircraft structures and fasteners.
Construction and Metal Fabrication: Applied in structural steelwork, railings, and enclosures.
Electronics and Machinery: Used in casings, frames, and mechanical assemblies requiring reliable threading.
Conclusion
Drill and tap machines play a crucial role in modern manufacturing, streamlining production while maintaining high accuracy and efficiency. With advancements in automation and CNC technology, these machines continue to enhance productivity and quality across various industries. Whether for small-scale workshops or large industrial operations, drill and tap machines remain essential for producing precise and durable threaded connections.