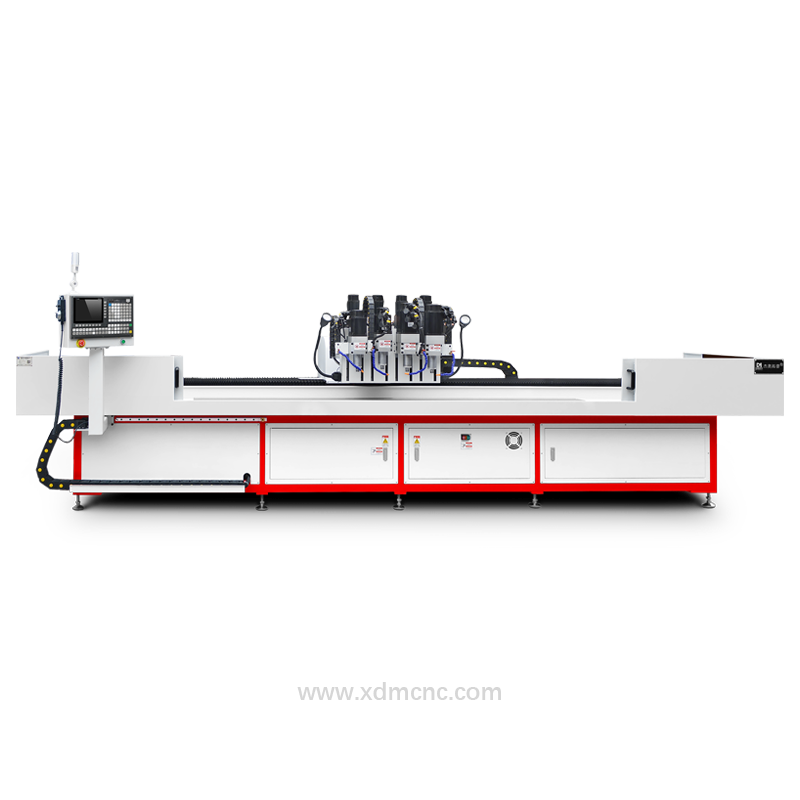
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) drilling machines have become an integral part of modern manufacturing. These machines are used to automate drilling operations in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, construction, and electronics. With the global advancement of smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0, the adoption of CNC drilling machines has surged. However, certain countries have emerged as leading users and manufacturers of CNC drilling machines.
1. China: The Global Leader
China is the largest user of CNC drilling machines, primarily due to its massive manufacturing sector. The country is known as the "world’s factory," producing a vast array of goods ranging from consumer electronics to industrial machinery. The Chinese government has been actively promoting smart manufacturing under the "Made in China 2025" initiative, further driving the adoption of CNC technologies. Chinese companies invest heavily in CNC automation to enhance productivity and reduce labor costs, making CNC drilling machines a crucial part of their industrial landscape.
2. United States: A Technological Powerhouse
The United States is another major user of CNC drilling machines, particularly in high-tech industries such as aerospace, defense, and advanced manufacturing. American companies like Boeing, Lockheed Martin, and General Motors rely on CNC drilling machines for precision engineering. The U.S. also has a strong domestic CNC machine tool industry, with companies like Haas Automation and Okuma America playing significant roles in the market. The country’s emphasis on innovation and automation ensures that CNC drilling machines are widely used to maintain global competitiveness.
3. Germany: Engineering Excellence
Germany is renowned for its engineering expertise and precision manufacturing. As a leading industrial powerhouse in Europe, Germany extensively utilizes CNC drilling machines in automotive production, industrial machinery, and electronics manufacturing. German brands such as Siemens, DMG Mori, and Trumpf are pioneers in CNC technology, contributing to the widespread use of these machines in both domestic and international markets. The country’s strong focus on automation and efficiency makes CNC drilling machines an essential part of its industrial infrastructure.
4. Japan: Innovation and Automation
Japan has long been at the forefront of CNC machining technology. The country is home to some of the world’s leading CNC machine tool manufacturers, including Fanuc, Mazak, and Okuma. Japanese industries, particularly in automotive and electronics, heavily depend on CNC drilling machines to maintain high precision and efficiency. With a declining workforce, Japan continues to invest in automation and robotics, further increasing the reliance on CNC technology.
5. India: An Emerging Market
India is rapidly growing as a major consumer of CNC drilling machines. With its expanding manufacturing sector and government initiatives like "Make in India," the demand for CNC technology is on the rise. Industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction are driving the adoption of CNC drilling machines. Indian manufacturers are increasingly investing in automation to improve production efficiency and compete in global markets.
6. South Korea: A High-Tech Manufacturing Hub
South Korea is a major player in electronics and automotive manufacturing, making CNC drilling machines an essential part of its industrial ecosystem. Companies like Samsung, Hyundai, and LG rely on high-precision CNC machines for production. South Korea’s focus on smart manufacturing and digital transformation has further accelerated the use of CNC drilling machines.
Conclusion
While CNC drilling machines are used worldwide, China stands out as the largest consumer due to its massive manufacturing base. The United States, Germany, Japan, India, and South Korea also play crucial roles in the adoption and advancement of CNC technology. As global industries continue to move towards automation and smart manufacturing, the demand for CNC drilling machines will only increase, making them a key component of modern production systems.