Drilling aluminum requires the right techniques and tools to ensure precision, efficiency, and a clean finish. Unlike steel, aluminum is a softer metal that can easily clog drill bits or produce rough holes if not handled correctly. This guide explores the best methods, tools, and tips for drilling aluminum effectively.
1. Choosing the Right Drill Bit for Aluminum
The selection of the correct drill bit is crucial to achieving a clean and precise hole in aluminum. Here are the best options:
High-Speed Steel (HSS) Bits – Standard choice for aluminum, offering durability and affordability.
Cobalt Drill Bits – Ideal for drilling harder aluminum alloys, providing higher heat resistance.
Carbide-Tipped Bits – Best for high-volume production or industrial applications due to extreme durability.
Step Drill Bits – Perfect for drilling progressively larger holes without changing bits.
2. Proper Drill Speed for Aluminum
Aluminum is softer than steel, requiring moderate speeds to avoid excessive heat buildup. The optimal drill speed depends on the bit size:
Small Bits (1/8” or smaller): 3,000 - 5,000 RPM
Medium Bits (1/8” - 3/8”): 1,500 - 3,000 RPM
Large Bits (3/8” and above): 500 - 1,500 RPM
Slower speeds help prevent overheating and bit wear, ensuring a clean cut.
3. Lubrication and Cooling Techniques
Using a lubricant reduces friction, minimizes heat buildup, and extends tool life. The best lubricants for drilling aluminum include:
Cutting Oil – Reduces heat and improves cutting efficiency.
WD-40 or Light Machine Oil – Prevents aluminum from sticking to the drill bit.
Water-Soluble Coolants – Used in high-speed drilling to dissipate heat effectively.
4. Drilling Techniques for Clean Holes
To achieve a smooth, burr-free hole in aluminum, follow these best practices:
a. Mark and Punch the Drilling Spot
Use a center punch and hammer to create a small indentation where you want to drill. This prevents the drill bit from wandering.
b. Use Firm and Steady Pressure
Apply consistent pressure without forcing the bit. Let the drill do the work to avoid deforming the metal.
c. Start with a Pilot Hole
For larger holes, begin with a smaller pilot hole (1/8” or smaller) before drilling to the final size. This ensures accuracy and reduces stress on the drill bit.
d. Clear Chips Frequently
Aluminum chips can clog the drill bit, reducing efficiency. Frequently retract the bit to remove debris and keep the hole clean.
5. Avoiding Common Drilling Mistakes
When drilling aluminum, be mindful of these potential issues:
Overheating: Prevent excessive heat by using lubrication and controlling drill speed.
Bit Slippage: Secure the workpiece properly using clamps to avoid movement.
Burr Formation: Use a deburring tool or sandpaper to smooth rough edges.
Work Hardening: If drilling takes too long in one spot, aluminum may harden and become more difficult to cut.
6. Best Drills for Aluminum
For optimal performance, consider using:
Drill Press – Provides stability and precise depth control.
Corded Power Drill – Delivers consistent torque and speed for aluminum drilling.
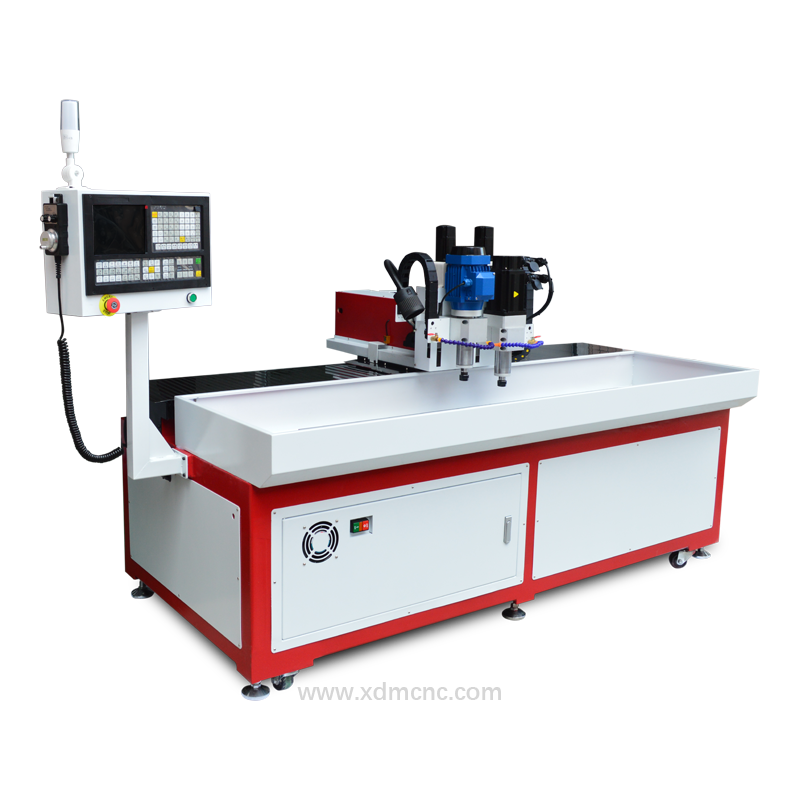
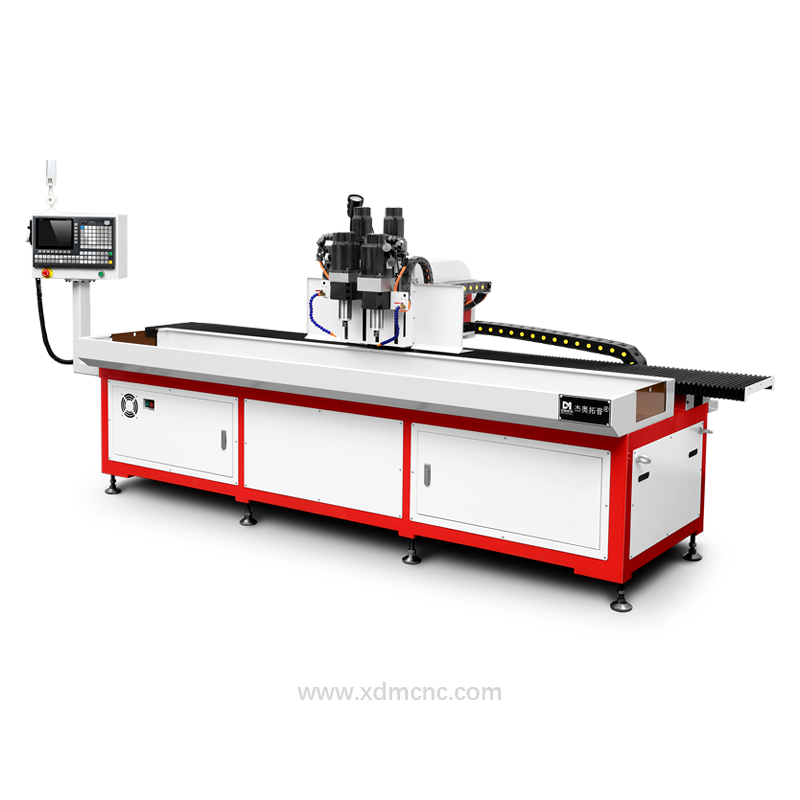
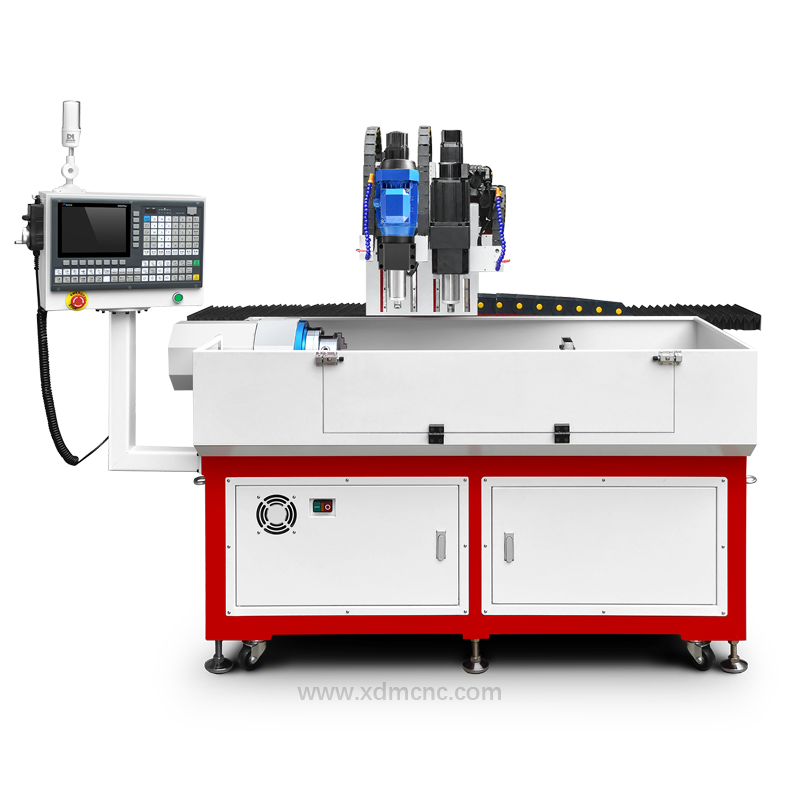
CNC Machines – Ideal for mass production or precision work.
Handheld Electric or Pneumatic Drills – Useful for portable drilling applications.
Conclusion
Drilling aluminum efficiently requires the right tools, techniques, and preparation. By choosing the appropriate drill bit, controlling speed, using lubrication, and following proper drilling methods, you can achieve clean, precise holes while extending tool life. Whether you're a DIY enthusiast or a professional machinist, following these best practices will enhance your aluminum drilling experience.
Keywords: best way to drill aluminum, aluminum drilling techniques, how to drill aluminum, aluminum drill bits, aluminum machining tips