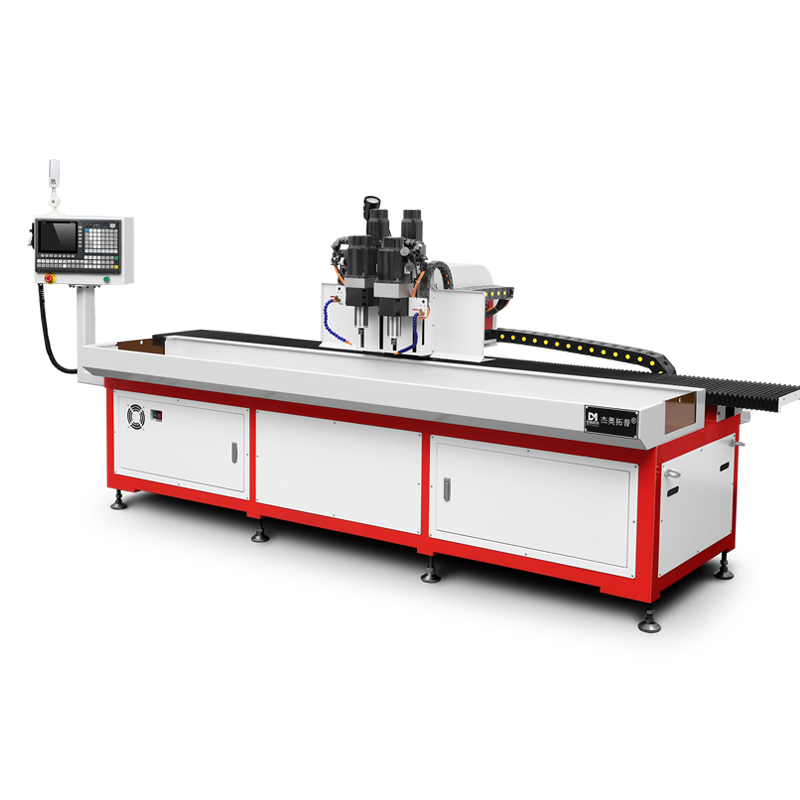
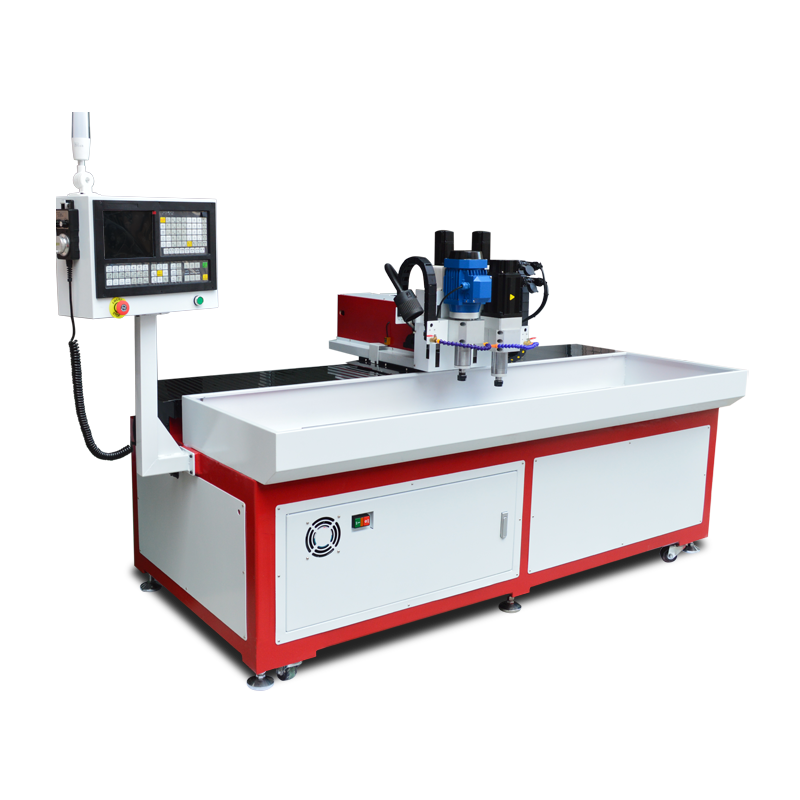
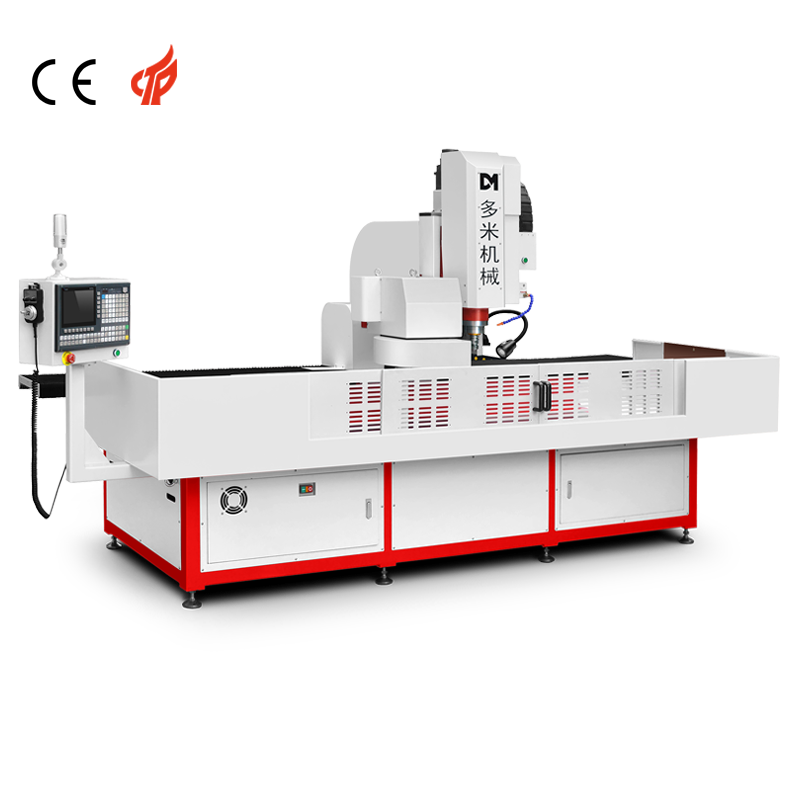
Introduction
Flow drilling and tapping machines combine the benefits of thermal drilling and threading, offering a comprehensive solution for creating high-strength, extruded bushings with integrated threads. This advanced metalworking technique enhances structural integrity and load-bearing capacity in thin-walled materials, making it indispensable in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction. By using friction-generated heat, flow drilling creates robust holes, while automated tapping ensures precision threading, eliminating the need for additional fasteners or inserts.
The Science Behind Flow Drilling and Tapping
Flow drilling and tapping machines operate on the principles of thermomechanical deformation and high-speed threading. The process follows several critical stages:
Friction Heating: A specialized tungsten carbide drilling tool rotates at high speeds (typically 2,000 to 5,000 RPM), generating localized heat through friction.
Material Deformation: The softened material is displaced rather than removed, forming an extruded cylindrical sleeve that extends the hole depth.
Hole Formation: The tool penetrates further, elongating the material and creating a work-hardened bore.
Tapping Process: A synchronized tapping tool threads the newly formed hole, ensuring a durable and precisely machined internal thread.
Surface Finishing: The tool withdraws, leaving a burr-free, high-strength threaded hole ready for assembly.
Advantages of Flow Drilling and Tapping Machines
These machines offer numerous benefits over traditional drilling and threading techniques:
Increased Thread Strength: The extruded sleeve significantly improves thread engagement, enhancing load-bearing capacity.
Material Efficiency: Since the process redistributes material rather than removing it, waste is minimized, and workpieces retain their original strength.
Structural Integrity: Work-hardening of the hole’s inner surface increases resistance to mechanical stress and fatigue.
Automation and Precision: Modern flow drilling and tapping machines integrate CNC control, ensuring consistent, high-accuracy results with minimal human intervention.
Reduction in Fasteners: By forming robust threaded connections, these machines eliminate the need for additional inserts, bolts, or rivets.
Versatile Material Compatibility: Effective on materials such as steel, stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and copper, offering flexibility in manufacturing applications.
Applications of Flow Drilling and Tapping Machines
This technology is widely used in various industries where high-strength, precision-threaded connections are essential:
Automotive Industry: Used in chassis manufacturing, engine components, and suspension systems, ensuring reliable connections.
Aerospace Engineering: Applied in lightweight aluminum and titanium structures where strong, lightweight fastenings are crucial.
Construction and Infrastructure: Enhances metal framework connections in buildings, bridges, and railway systems.
Industrial Machinery: Enables precise assembly in heavy-duty equipment, reducing maintenance and improving reliability.
Renewable Energy: Strengthens critical joints in wind turbine structures and solar panel frames, optimizing longevity and durability.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the advantages, some challenges must be addressed:
Tool Wear: The high-speed rotational force results in gradual wear of tungsten carbide tools, requiring periodic replacement.
Material Limitations: Brittle materials may not be suitable for this process due to thermal stress and potential cracking.
Initial Equipment Costs: Advanced CNC-integrated flow drilling and tapping machines require significant investment but offer long-term cost savings through efficiency gains.
Conclusion
Flow drilling and tapping machines represent a significant advancement in precision manufacturing, delivering high-strength, extruded-threaded holes with exceptional efficiency. Their adoption in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction highlights their importance in modern engineering. As technology continues to evolve, further enhancements in tool design, automation, and process optimization will solidify the role of flow drilling and tapping machines as essential components of high-performance manufacturing solutions.